Though it has several key constraints, the Metrorail System’s capacity compares favorably with its peers and even out-performs them in several key measures.
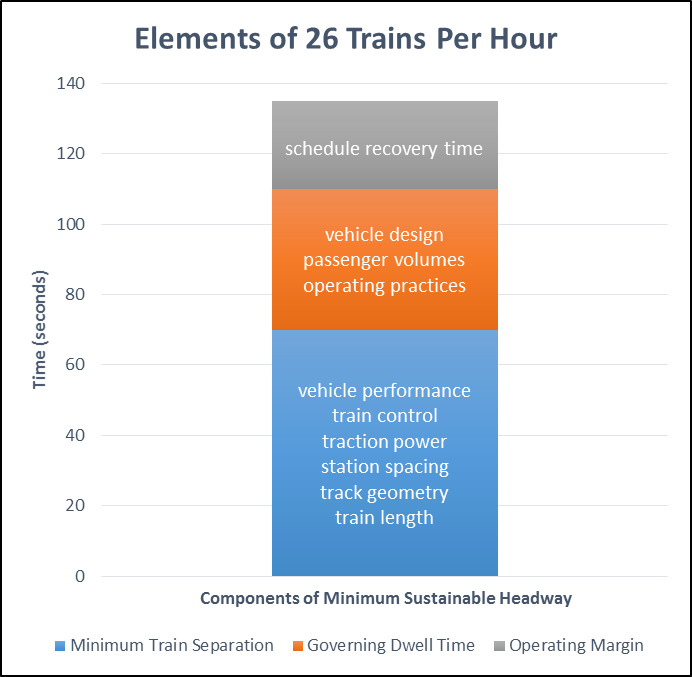
In a previous post, we explained that Metro doesn’t schedule more than 26 trains per hour at any point in an effort to balance reliability with high capacity operations. But it also raises some interesting questions: How does Metrorail’s capacity compare to peers? How does Metrorail compare to its peers in terms of train throughput and what are the specific constraints that prevent trains from operating more frequently? Are there any ways to increase the capacity of the existing system beyond 26 trains per hour?
We developed a white paper (PDF) to answer those questions. Some of the findings might surprise some Metroskeptics or armchair transit planners, but Metrorail has among the highest capacity infrastructure in the industry, which – when in a state of good repair – allow it to outperform its peers in a number of key areas.
 Read more…
Read more…
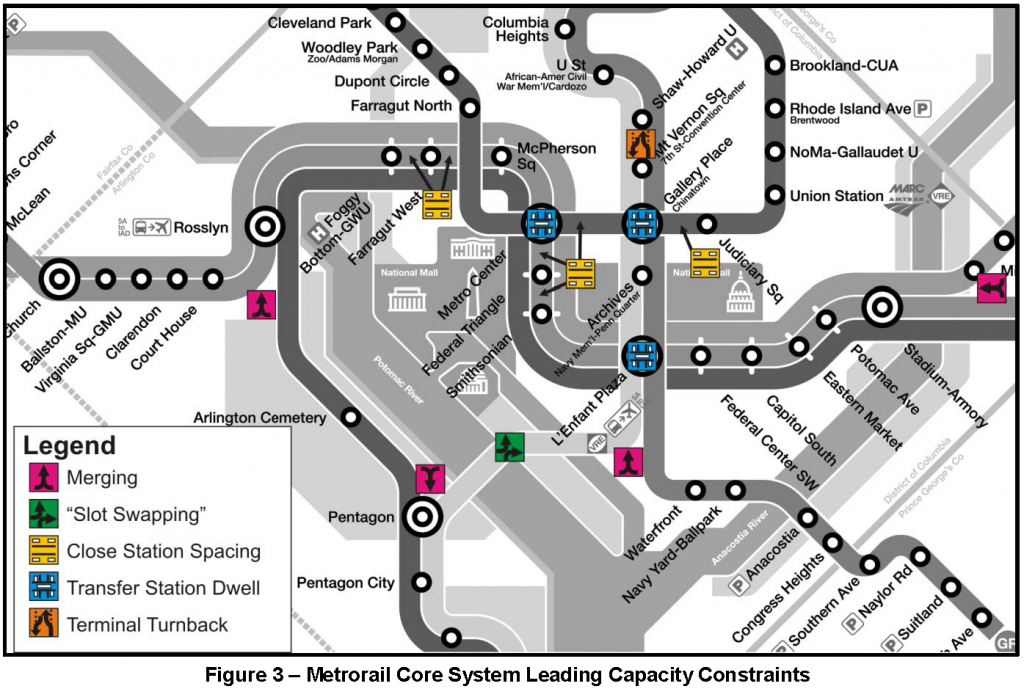
Why can’t Metrorail reliably operate more than 26 trains per hour per direction? A 2001 study defined the basis for determining this constraint.
Although it has been known for years, the July 2014 opening of the Silver Line and corresponding reduction of rush hour Blue Line service highlighted that Metro cannot schedule more than 26 trains per hour (or a train every 2-2.5 minutes) across any point in its rail network. Though it’s been discussed many times through the years, let’s explain this limit in detail now.
Read more…
DDOT’s 16th Street transit plan will benefit Metrobus riders, drivers and taxpayers alike and could “break even” in just a year and a half.
We know the problems with buses on 16th Street NW: overcrowding, slow speeds, lengthy boarding times, and bunched buses. While both the District Department of Transportation (DDOT) and Metro have made several small but important improvements in the past two years to improve traffic flow and increase bus capacity on 16th Street, both agencies realize that more needs to be done. Now, after a year of detailed study in partnership with Metro, DDOT has developed a set of recommendations (PDF) that will save time and improve the customer experience in the coming years. As an added bonus, it comes with a relatively cheap price tag, yielding great value for taxpayers.
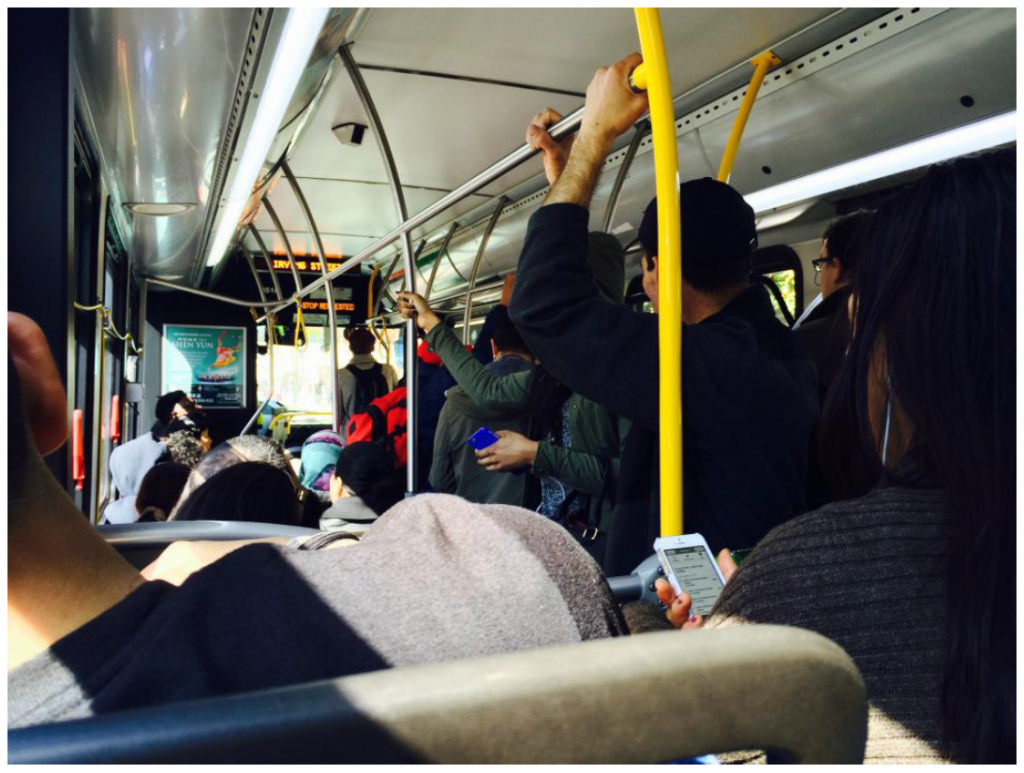

Riders aboard a crowded S-Line bus (click for study information)
Read more…
We explore questions about WMATA’s creation and how decisions are made in our “Metro 101” series.

Metrorail groundbreaking at Judiciary Square (December 9, 1969)
Why was WMATA created?
WMATA was founded in 1967 to serve 3 primary functions:
- To plan, develop, finance and “cause to be operated” improved transit facilities as part of a balanced regional transportation system;
- To coordinate the operation of the public and privately owned or controlled transit facilities into a unified regional transit system;
- To serve “other regional purposes” as needed.
Read more…
Secretary Foxx has issued his direction that Metro cannot consider any new rail expansion right now, and WMATA agrees! So much so that we wrote it into our strategic plan back in 2013. Earlier this fall, the Prince William County’s Board of Supervisors heard from WMATA about the importance of fixing Metro’s core before considering any expansion.

The Silver Line’s Phase 2 extension from Wiehle-Reston East to Dulles Airport and Loudoun County could be the last for decades to come. (photo credit: Ryan Stavely, Flickr)
As the region grows, so does the pressure for extensions of Metrorail. The requests are frequent and common: “Extend Metro to BWI! to Centreville! to Waldorf! to Fort Belvoir!” We’ve heard and even modeled most of these requests. For a system that’s shaped and contributed tremendous economic value to the region, it only makes sense that communities outside of its immediate reach want improved access to it. WMATA Director of Planning Shyam Kannan recently took the opportunity to discuss the potential for the extension of Metrorail into Prince William County. With 80% of today’s Metrorail trips going to or through the system’s core (PDF), he noted that major core capacity improvements must be made prior to considering any additional rail extensions. While addressing core capacity has been a major part of Momentum, including initiatives like the 8-car train program, core stations, and New Blue Line Connections, the plan remains largely unfunded. With safety and state of good repair needs as Metro’s top priorities and core capacity relief put off indefinitely, any potential extensions (if they happen) are likely decades away from being built.
Read more…
Categories: Strategies Tags: BRT, commuter rail, core capacity, corridors, expansion, land use, LRT, Metro 2025, Metrorail, Momentum, policy, Streetcar, tod, transit-oriented development
In the past 17 years, Metrobus has faced dual challenges: increased competition and increased roadway congestion.
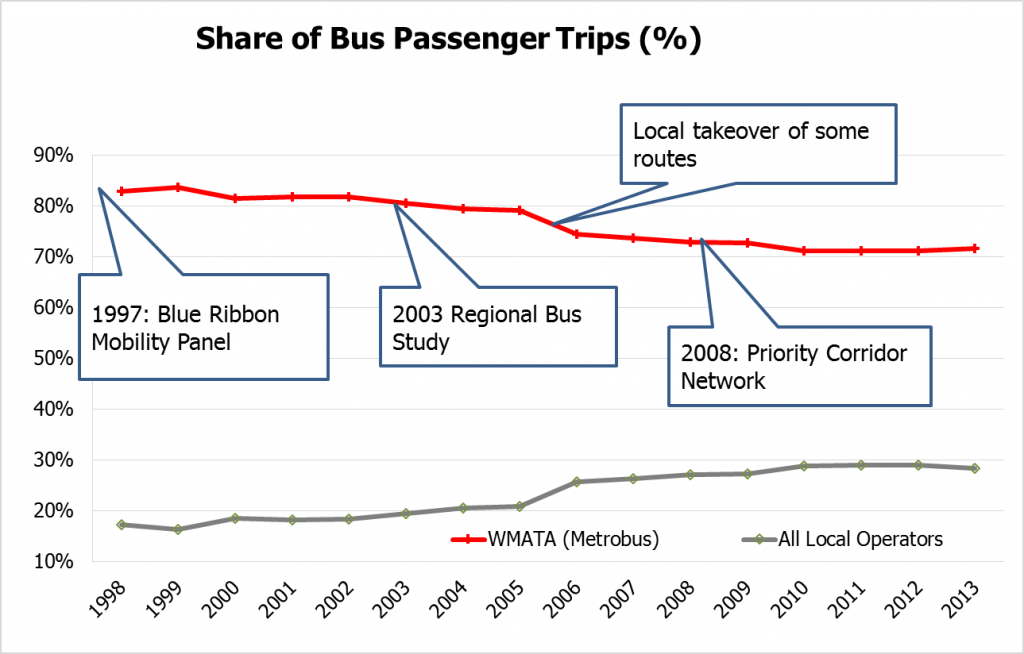
A past post discussed the role of the 1997 Blue Ribbon Mobility Panel in resetting the regional role and funding structure for Metrobus. In the decade-plus since then, several trends have emerged: Local operators are rolling out more and more bus service, and buses are getting slower.
Read more…
A new Virginia study (PDF) finds that Metro and other transit operators carry a major portion of all cross-Potomac travel in a just a few crossings, using far less space than the 57 highway bridge lanes that carry the rest. If built, an expanded bridge crossing will need transit to maximize its ability to move people across the river.

Transit’s Role is Critical
While some media outlets focused on the study’s highway expansion recommendation, the presentation acknowledged that Metro, VRE, and other bus operators plays a major role in the movement of people across the river from Virginia to DC in the core of the region. Seeing that, we thought we we’d drill down further to estimate how many people are actually crossing the river, using which bridge, and by what mode. Supplementing the study with available transit ridership data and vehicle occupancy data (PDF), we arrived at the following estimates: Read more…
Categories: Impact Tags: bus, commuter bus, commuter rail, dc, maryland, Metrobus, Metrorail, mode share, Potomac River, travel patterns, Virginia, VRE
Transit expansion is in demand but Metrorail, light rail, and other high capacity transit projects can be expensive to build, operate and maintain. With limited resources to invest, our region must ensure that these projects serve the most robust transit markets and are supported by strong transit friendly policies.
Informed by our peers and local performance measures, Metro is developing guidelines that the region can use to inform development of high capacity transit projects. As we’ve explored previously, there’s much more to transit expansion than Metrorail. In fact, due to the cost associated with Metrorail expansion along with existing land uses and built environment in much of the region, most of our future high capacity transit projects will be made up of other transit modes. But what is the best way to decide what mode best fits each corridor? The goal of the expansion guidelines is to inform those decisions.

Development in Arlington’s Rosslyn-Ballston Corridor has validated initial and ongoing investments in Metrorail. (source: Arlington County)
A literature and peer review included policy documents from BART (PDF), the Bay Area Metropolitan Transportation Commission, Florida DOT, Virginia DRPT, Federal Transit Administration (PDF), and research from the University of California Transportation Center (UCTC). The review found that ridership, density, the presence of walkable streets and sidewalks, local plans and policies, and cost effectiveness are the most relevant criteria to evaluate transit projects and that rigorous performance targets are needed to support each transit mode. Read more…
Categories: ConnectGreaterWashington Tags: BART, BRT, corridors, DRPT, Light Rail, Metrorail, plans, ridership, Streetcars, tod, transit-oriented development
The majority of late night bus boardings are in DC, focused along the 14th/16th Streets NW corridor.
As we’ve mentioned before, Metro is conducting a study examining late night bus service in the region. An initial step was to assess where the late night boardings are happening in order to determine which might be the best locations to focus in-person survey efforts. Below is a map showing the locations of the top 100 locations where riders board Metrobus from 11pm-4am each night. Rather than reflecting the total ridership of a stop, the magnitude of the circles on the map reflect that location’s share of overall late night bus ridership.
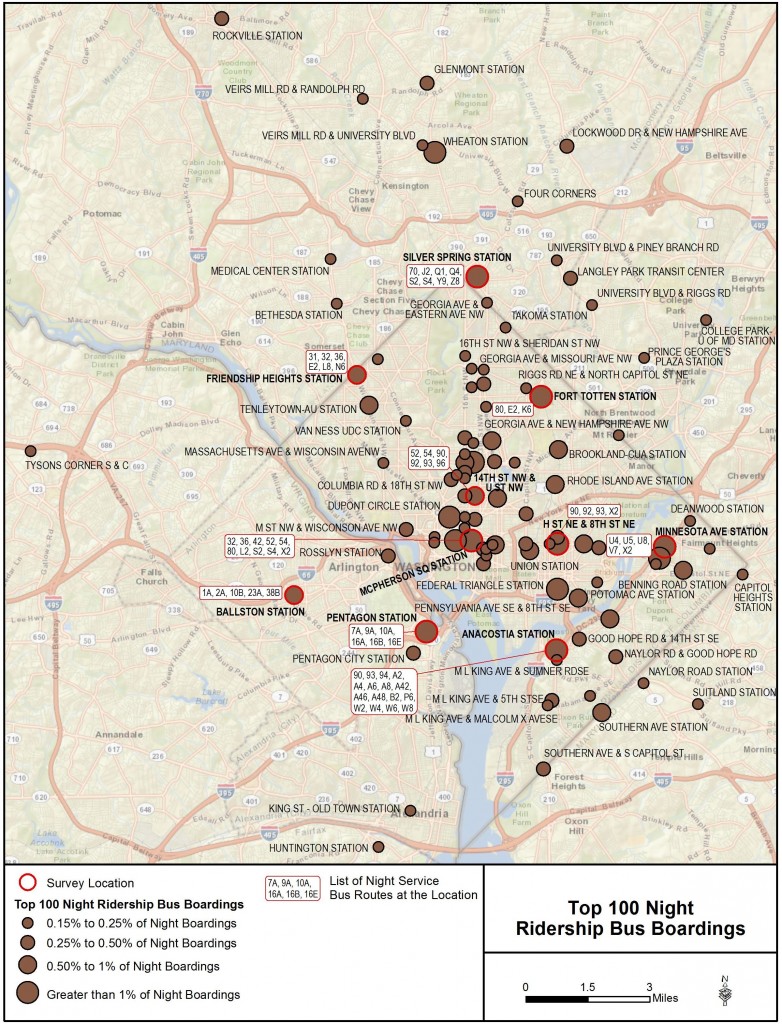
Top 100 Late Night Metrobus Boarding Locations*
Some notes on the map:
- Almost all of the major bus boarding locations (those with more than 1% of the total) are at Metrorail Stations, even though Metrorail stops operating just one hour into the late night period on weeknights.
- Not surprisingly, most of the boardings are in DC, many of which are concentrated in the 16th/14th St NW corridor from downtown to Columbia Heights.
- The data only reflect Metrobus boardings, so if boardings on local operators such as DC Circulator are added, the total numbers of late night bus boardings would be higher than what is shown here.
- Of course this only tells us where the riders are boarding, not necessarily where they’re going; we are investigating that as part of the study.
What do you see that stands out?
* Note that Southern Avenue Metro Station replaced 14th & U Street as an in-person rider survey location.
Known to most Americans for its famous wine varieties, Bordeaux is also an innovator in surface transit technologies that allow for wireless tram operations on its downtown streets.
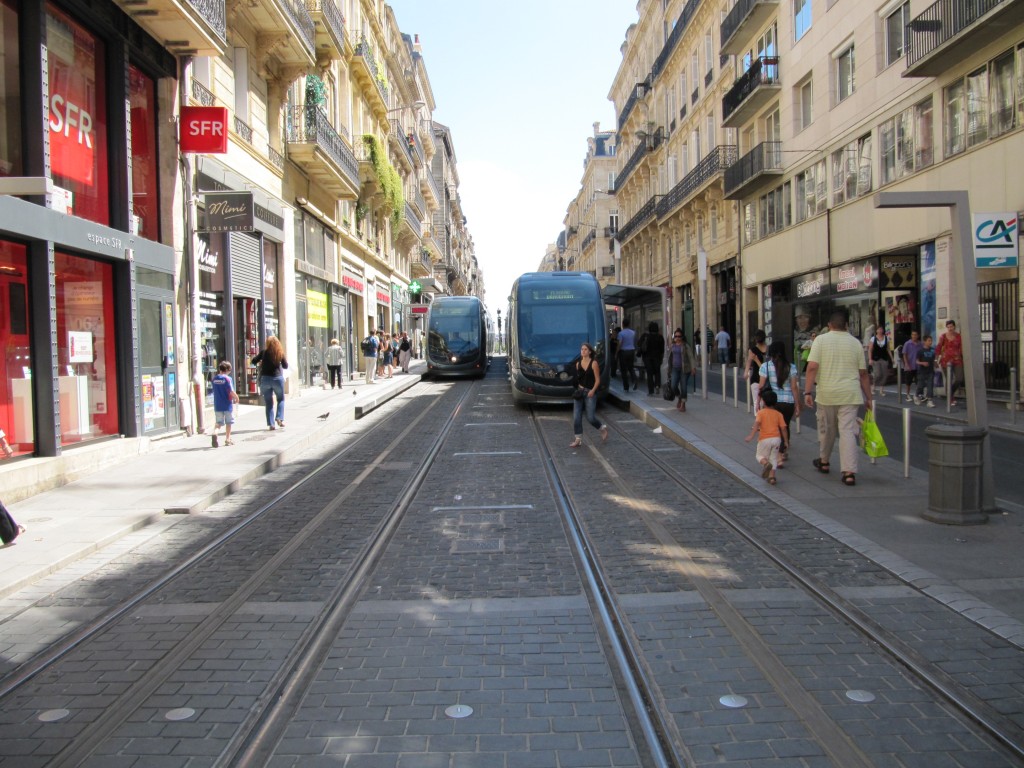

Two wireless trams serve paired center city station platforms
On a visit to Bordeaux in 2010, I drank its fabulous wines, walked along the Garonne, enjoyed its comfortable summer climate… and took note of its innovative trams (light rail/streetcar). You might be thinking “trams… really?” Yes! While most systems are powered by overhead wires, when it opened in 2003 Bordeaux’s system was the only modern example of ground level powered wireless trams in the world. The proprietary APS system allows for typical overhead wire operation in the areas outside the central city and operation with ground-level power (see photo below) inside it in order to preserve unobstructed views in the old city. Although the system initially had reliability problems, it now seems to be performing well.
Read more…











Recent Comments