The year 2040 may seem distant  and removed, but in the context of transit planning, it is right around the corner. Metro’s Office of Planning is in the process of developing the 2040 Regional Transit System Plan (RTSP), which will outline a comprehensive regional transit network to prepare the region’s transit system for continued growth.
and removed, but in the context of transit planning, it is right around the corner. Metro’s Office of Planning is in the process of developing the 2040 Regional Transit System Plan (RTSP), which will outline a comprehensive regional transit network to prepare the region’s transit system for continued growth.
The RTSP, along with other elements that may be identified in the future, will need to be evaluated as necessary to meet the demands in the future. The plan includes a combination of core system improvements, which are included as part of Metro 2025 above, as well as system connectivity and expansion projects. Most importantly, it combines all modes in the region’s transit system, whether or not Metro will build or operate them. The strategies in the plan are designed to both serve existing areas better and provide service to new areas, helping to realize Region Forward’s vision of regional activity centers with transit options that improve regional mobility, enhance commerce and competitiveness, and have environmental and health benefits for generations to come.
Read more…
Portions of Momentum are  already being executed, meaning that elements in this strategic plan under Metro’s control are already in implementation mode. Engineering work is well-underway to support some of the immediate and near-term investments and innovations to carry the system to the year 2025. Some of the projects and their dates of completion or anticipated completion include the following:
already being executed, meaning that elements in this strategic plan under Metro’s control are already in implementation mode. Engineering work is well-underway to support some of the immediate and near-term investments and innovations to carry the system to the year 2025. Some of the projects and their dates of completion or anticipated completion include the following:
Metro’s staff and Board are already laying the financial underpinnings to execute the strategic plan. In 2013, the Board approved Metro’s multi-year capital and operating budgets. While continuing laser-like focus on safety improvements and the rebuilding of the existing system, the FY 2014-2019 Capital Improvement Program (CIP) includes a number of significant investments that lay the groundwork for the implementation and execution of Metro 2025, which is described in the following section and later in this document.
Read more…
Momentum builds upon and advances  a number of regionally significant planning studies that are either recently completed – or underway. They include:
a number of regionally significant planning studies that are either recently completed – or underway. They include:
- Region Forward: A vision for the DC region created by the MWCOG. It addresses the interrelated challenges of population growth, aging infrastructure, traffic congestion, energy costs, environmental impacts, affordable housing and sustainable development, as well as disparities in education, economics and health (2010)
- Economy Forward: A companion piece to Region Forward that reinforces the importance of transit to the region’s overall competitiveness (2012)
- Financially Constrained Long-Range Transportation Plan (CLRP): The region’s official long-range transportation plan that outlines the priority projects to be implemented in the region between 2012 and 2040 as prioritized by the Transportation Planning Board (TPB) and local jurisdictions (2012)
Read more…
The National Capital Region Transportation Planning Board (TPB), the region’s Metropolitan Planning Organization (MPO), adopts the region’s constrained long-range plan (CLRP) annually. Only projects included in this regional transportation plan are eligible for federal funding, and since 1991, federal law requires the CLRP to be constrained financially. This regional transportation plan includes only projects that are reasonably expected to be fully funded.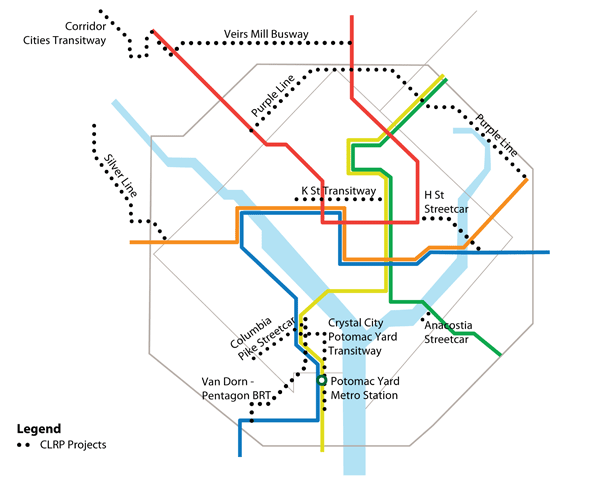
Read more…
Momentum employed a multi-pronged outreach  and feedback gathering strategy, including both conventional and modern tools. Metro staff gathered input to inform a draft plan and subsequently, gathered feedback on the plan prior to finalizing it. Metro staff heard from almost 12,000 stakeholders during the outreach process through the following tools. The input has informed Metro’s understanding of the public’s short- and long-term needs. Read more…
and feedback gathering strategy, including both conventional and modern tools. Metro staff gathered input to inform a draft plan and subsequently, gathered feedback on the plan prior to finalizing it. Metro staff heard from almost 12,000 stakeholders during the outreach process through the following tools. The input has informed Metro’s understanding of the public’s short- and long-term needs. Read more…
Metro is the nation’s most 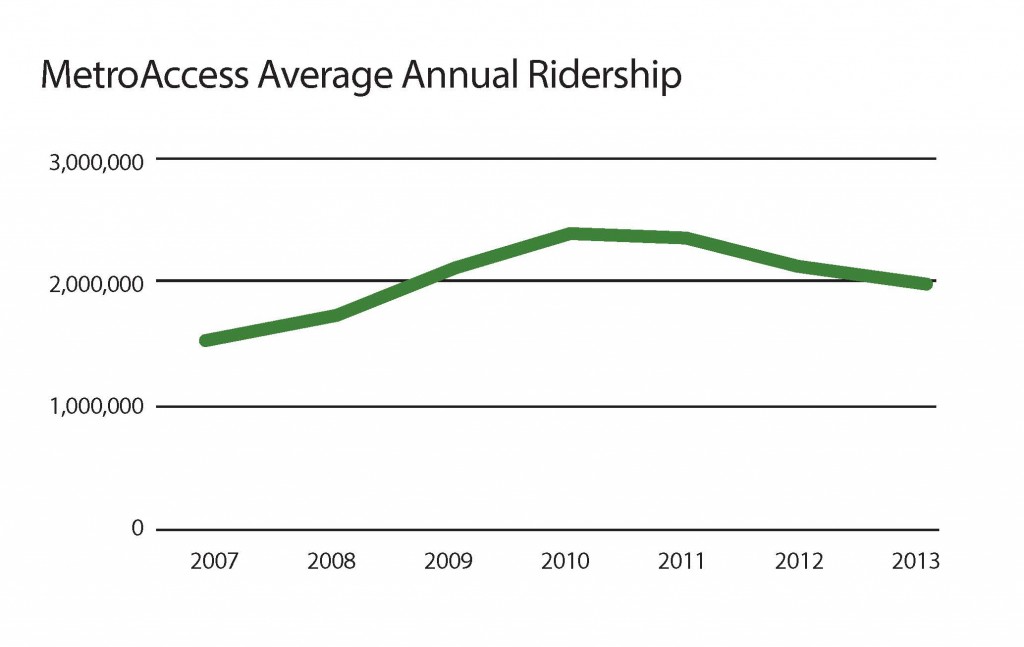 accessible large transit system. All 86 Metrorail stations have elevators and the new 7000-series rail cars are designed to maximize accessibility. Metrobus operates 1,100 fully accessible buses, most of which are low-floor and ramp-equipped and all of which have automated stop announcements. Numerous other changes have been made by Metro to maximize usability so that many customers with disabilities are able to use Metrobus and Metrorail for some of their travel. However, inadequacies such as the lack of curb cuts, sidewalks and traffic signals impact disabled customers’ ability to use Metrorail and Metrobus. MetroAccess serves these trips and others and presently provides about two million trips per year.
accessible large transit system. All 86 Metrorail stations have elevators and the new 7000-series rail cars are designed to maximize accessibility. Metrobus operates 1,100 fully accessible buses, most of which are low-floor and ramp-equipped and all of which have automated stop announcements. Numerous other changes have been made by Metro to maximize usability so that many customers with disabilities are able to use Metrobus and Metrorail for some of their travel. However, inadequacies such as the lack of curb cuts, sidewalks and traffic signals impact disabled customers’ ability to use Metrorail and Metrobus. MetroAccess serves these trips and others and presently provides about two million trips per year.
Read more…
In 1967, the federal government passed  a bill to create the Washington Metropolitan Area Transit Authority (Metro). The interstate Compact was signed by the District of Columbia, the Commonwealth of Virginia, and the State of Maryland. Metro continues to be chartered by this interstate Compact. Among all transit providers in the Washington region – which number more than 15 – Metro is unique in that it serves both states and the District. It provides the only truly regional transit network.
a bill to create the Washington Metropolitan Area Transit Authority (Metro). The interstate Compact was signed by the District of Columbia, the Commonwealth of Virginia, and the State of Maryland. Metro continues to be chartered by this interstate Compact. Among all transit providers in the Washington region – which number more than 15 – Metro is unique in that it serves both states and the District. It provides the only truly regional transit network.
In the late 1970s, Metro trains carried just over 100,000 passengers a day and served hundreds of thousands of passengers on the bus system. Since then, most rail stations in the core of the system have seen ridership more than double. As depicted below, rail average weekday ridership system-wide has gone from just over 500,000 in 1990 to almost 750,000 today, or 220 million trips annually, while weekday bus ridership has stayed at a stable level of roughly 450,000 daily trips, or 134 million trips annually. Read more…
 Strategic planning is the process of determining what an organization does, where it wants to be and how it plans to get there. Organizations with well-defined strategic plans have the distinct advantage of clarity of common direction. It offers discipline, focus, and results-orientation, enabling the entire enterprise to focus its talents and energies and to measure achievements against expectations and potential constraints. At Metro, it also provides leaders clear direction for prioritizing decisions around improvements, investments, expansion, operations, and maintenance.
Strategic planning is the process of determining what an organization does, where it wants to be and how it plans to get there. Organizations with well-defined strategic plans have the distinct advantage of clarity of common direction. It offers discipline, focus, and results-orientation, enabling the entire enterprise to focus its talents and energies and to measure achievements against expectations and potential constraints. At Metro, it also provides leaders clear direction for prioritizing decisions around improvements, investments, expansion, operations, and maintenance.
Metro needs a strategic plan for all of the above reasons and more. The organization is implementing hundreds of improvements to rehabilitate the system via MetroForward and instilling management discipline to the organization through the General Manager/CEO’s business plan. These efforts will have positive effects in the near term, but will be insufficient to prepare the system and organization for the challenges to come. Read more…
 and removed, but in the context of transit planning, it is right around the corner. Metro’s Office of Planning is in the process of developing the 2040 Regional Transit System Plan (RTSP), which will outline a comprehensive regional transit network to prepare the region’s transit system for continued growth.
and removed, but in the context of transit planning, it is right around the corner. Metro’s Office of Planning is in the process of developing the 2040 Regional Transit System Plan (RTSP), which will outline a comprehensive regional transit network to prepare the region’s transit system for continued growth.







Recent Comments