Investing in the region’s activity centers that have high-capacity, high-frequency transit and enhancing them as proposed in the Place+Opportunity report is part and parcel to preserving the economic competitiveness of the region AND creating a financially-sustainable Metrorail system.
(This post is part of a multi-part series about  ConnectGreaterWashington and the study’s application of land use as a transportation strategy. Part one of the series discussed why Metro cares about land use and the potential benefits of assessing growth from a regional perspective. Part two below outlines the study’s goals, assumptions, and approach.)
ConnectGreaterWashington and the study’s application of land use as a transportation strategy. Part one of the series discussed why Metro cares about land use and the potential benefits of assessing growth from a regional perspective. Part two below outlines the study’s goals, assumptions, and approach.)
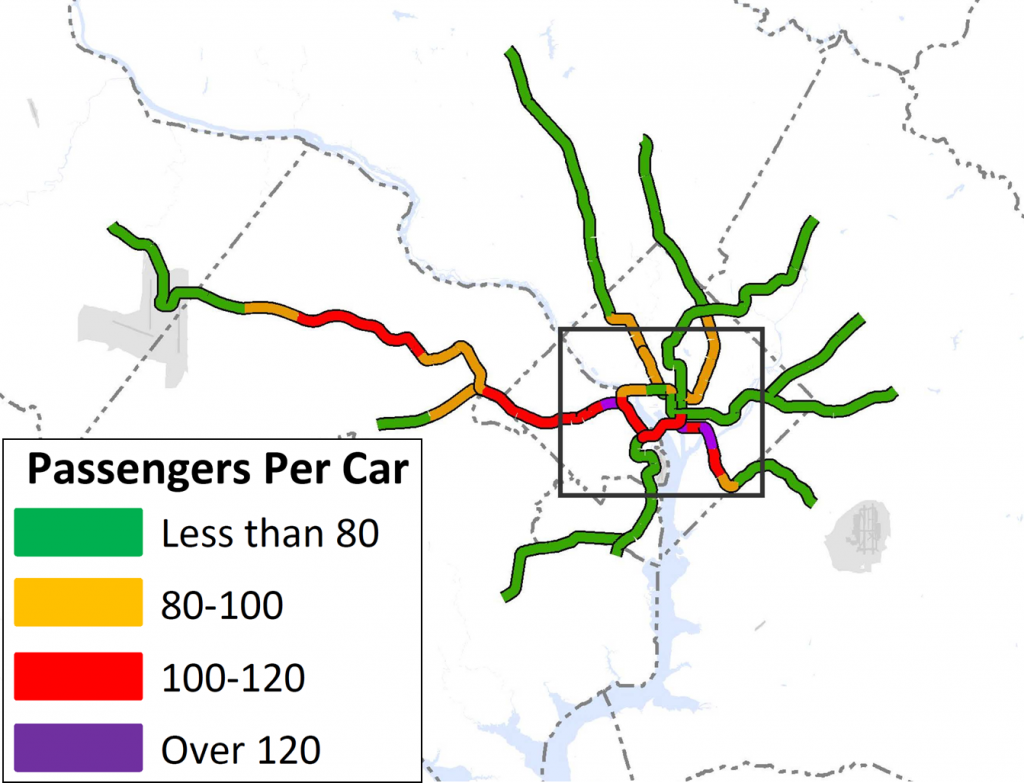
WMATA planners posited that changes to local jurisdictions’ and/or the region’s approach to land use and other policies would enable better use of the transportation system this region already built rather than require it to spend billions on new projects. Money is not falling from trees to expand transit — the region hasn’t even agreed to fund enough rail cars to run all eight car trains! So, if the region can’t (or won’t) invest in transit to keep up with growth, then we need to carefully evaluate how the growth we are forecasting can use the infrastructure we already have. Can the region’s growth, rather than necessitate billions of dollars in new infrastructure, be thoughtfully planned to better utilize the roadway and transit systems we already have? What would that mean to the region, its finances, and to Metro’s operating subsidies that its funding partners pay annually?
We developed an Executive Summary (pdf) that summarizes our approach and findings. These posts are infinitely more detailed, but you can certainly glean the key points from the Executive Summary.
The Basics
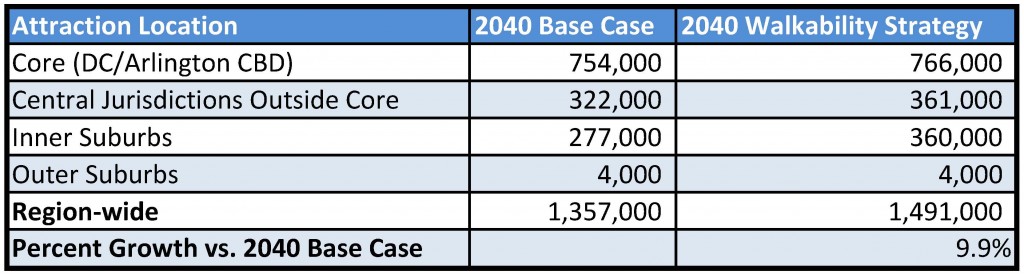
First and foremost, this study did not seek to develop an optimal land use or in any way socially engineer where future population and jobs should go. These are “what if” scenarios to provide context, data, and information to citizens, decision makers, and elected officials as the region grapples with future job and population growth, demand for transit, and development of walkable communities. This study sought to consider where future growth could go, and worked only with the regional growth anticipated to exist in this region in forecasts from 2020 through 2040. The modeling left existing jobs and population exactly where they exist today and was mindful that anything already in the development pipeline was far enough along to be assumed as “in place”.
Second, we followed the place types defined in Place+Opportunity as they were identified, developed, and defined by local jurisdictional planning staff and the Metropolitan Washington Council of Governments (MWCOG). Why? Because we wanted this study to be as realistic as possible and remain true to the nature of the activity centers and the jurisdictions that informed their types and densities. Additionally, Place+Opportunity was completed recently (2014) and had significant support and direct input from the jurisdictions and the region.

Place+Opportunity Place Types
Read more…




 )
)
Recent Comments