Ridership Before and After the Blizzard of 2016
What happens to ridership when a major snowstorm closes Metro?
The blizzard at the end of January dumped around two feet of snow on the Washington region over the course of a few days, making it the fourth-largest snowstorm in D.C. in over a century. To protect equipment, for the safety of employees and riders, and to focus on cleanup efforts, Metro ceased all operations for over three days. The Federal Government and schools were closed.
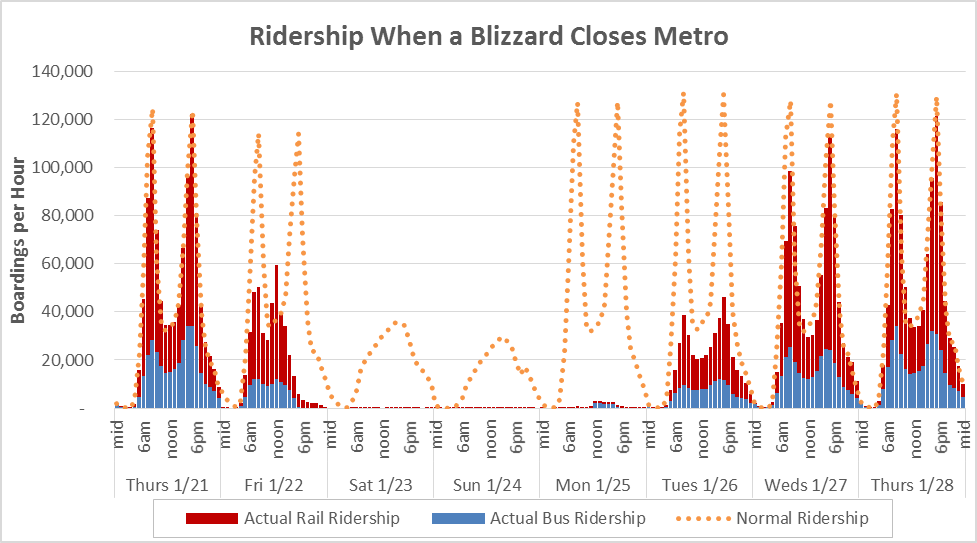
The chart below tells the story of the blizzard from a ridership perspective. Actual bus and rail ridership by hour is shown as blue and red, with the orange dotted line showing a typical pattern from two weeks prior in January.
Even before the snowflakes began falling on the afternoon of Friday, January 22, Metro’s ridership was impacted. That day, riders adjusted their normal routines by staying home, teleworking, or leaving early. The morning’s peak was half of normal. By Friday night, bus and rail operations ceased. No service operated Saturday or Sunday. Very limited bus and rail service was offered for a few hours on Monday, January 25 as cleanup and recovery began. Fares were not charged on rail, so we recorded very few transactions.
We recovered gradually on Tuesday and Wednesday, and nearly fully by Thursday, even as many school systems remained closed.
In the end, total ridership losses were estimated to be about 2.9 million boardings over five days, 1.6 million on rail and 1.3 million on bus. Bus took a proportionately bigger hit than rail given service restrictions from icy and unsafe road conditions.
What do you see in these numbers? Also, feel free to download the underlying data (.xlsx, 40kb) for yourself.



Recent Comments