What Metro 2025 Means to Virginia
Metro 2025 would bring significant benefits to northern Virginia, allowing the region to thrive economically while preserving regional vitality.
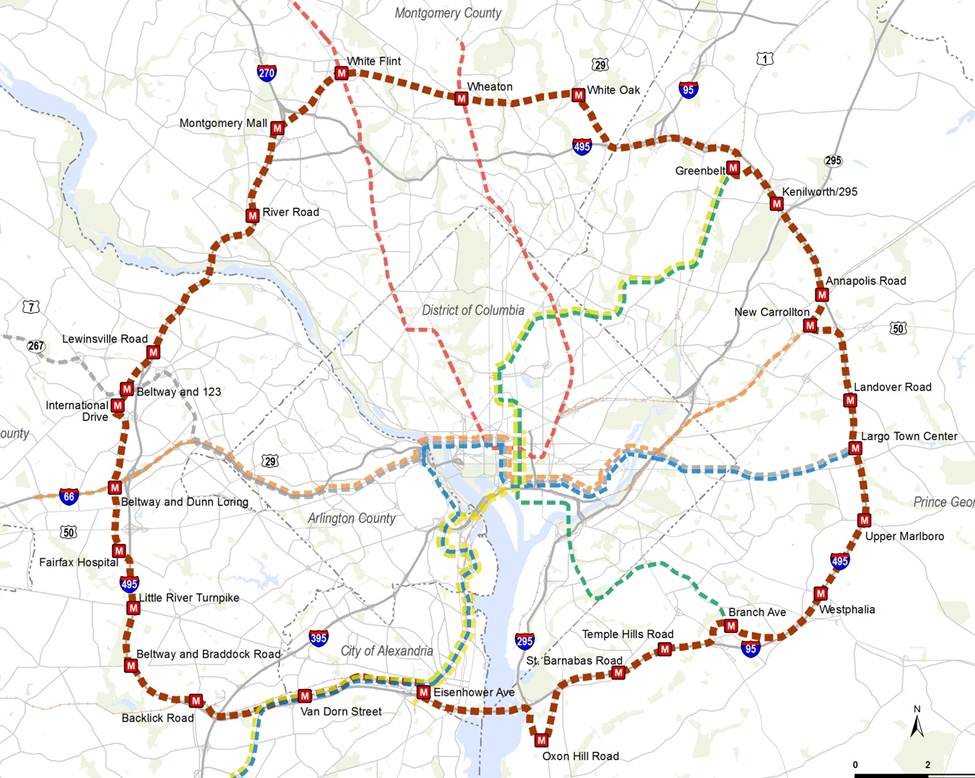
Think Metro’s Momentum plan is all about “downtown?” Think again! Our seven Metro 2025 initiatives – from eight-car trains to bus-only lanes will bring dramatic improvements to the quality of life and transportation to northern Virginia.
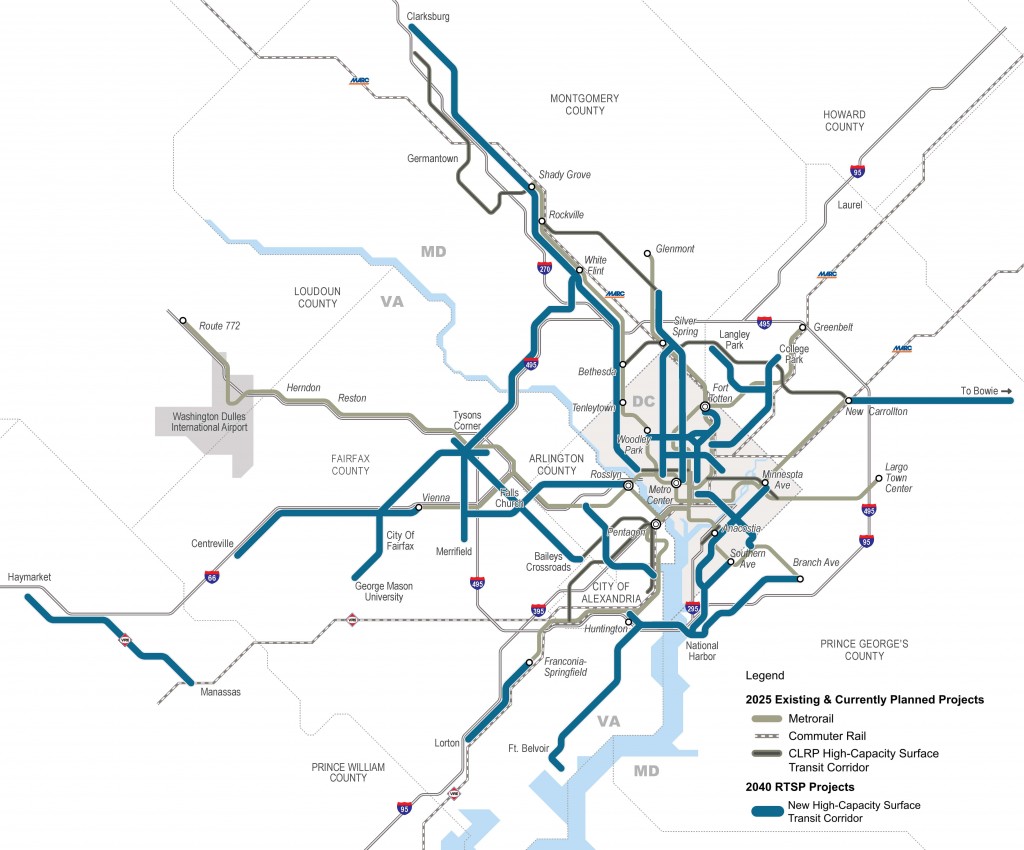
Supports Virginia Transit Projects
Virginia is planning big for transit, which is great – but all of the planned projects rely on a robust Metrorail and Metrobus “backbone” to succeed:
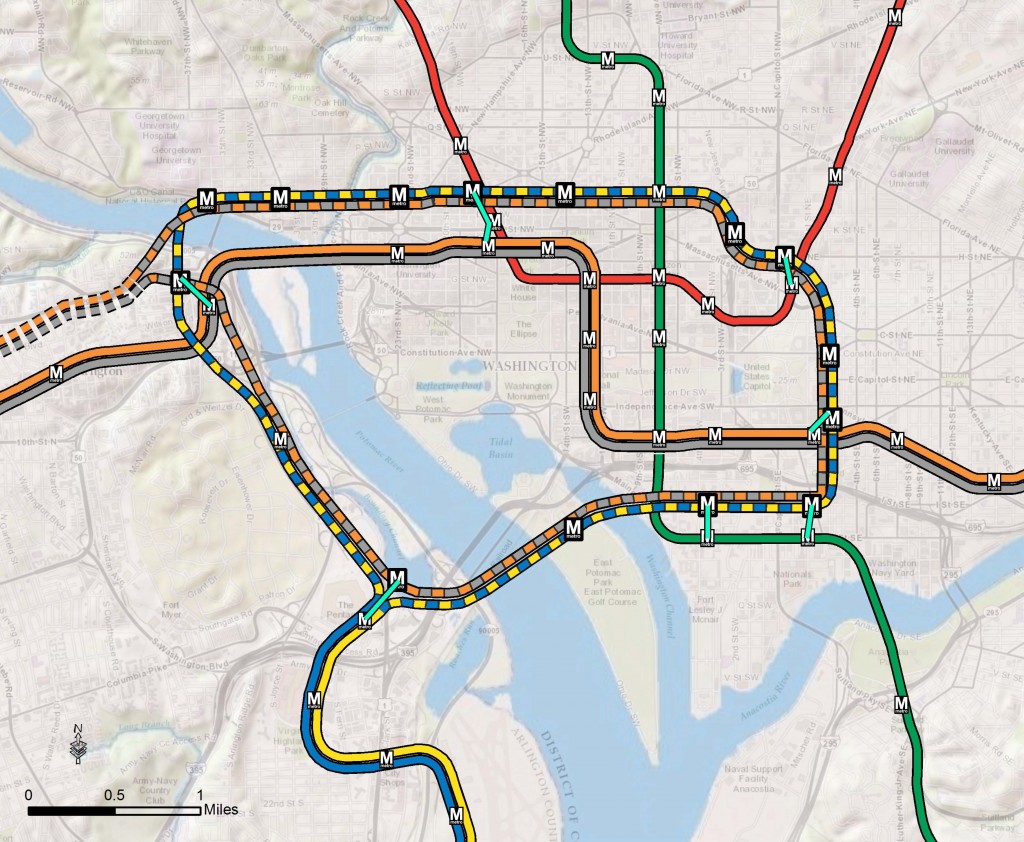
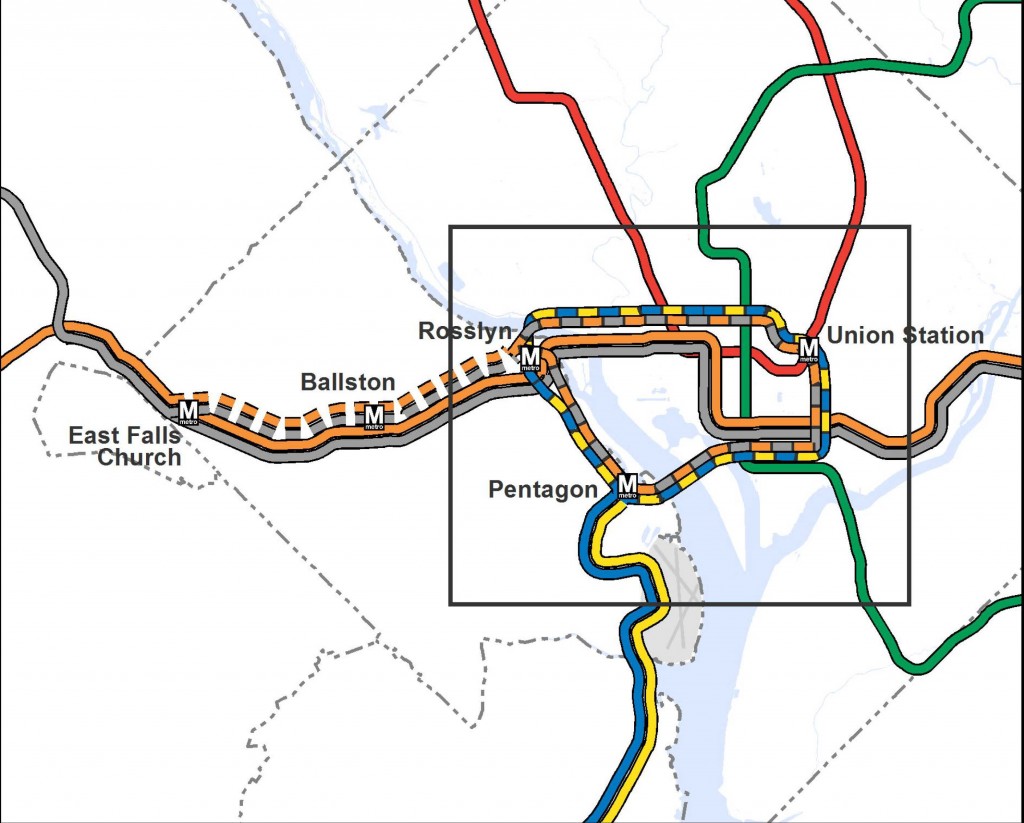
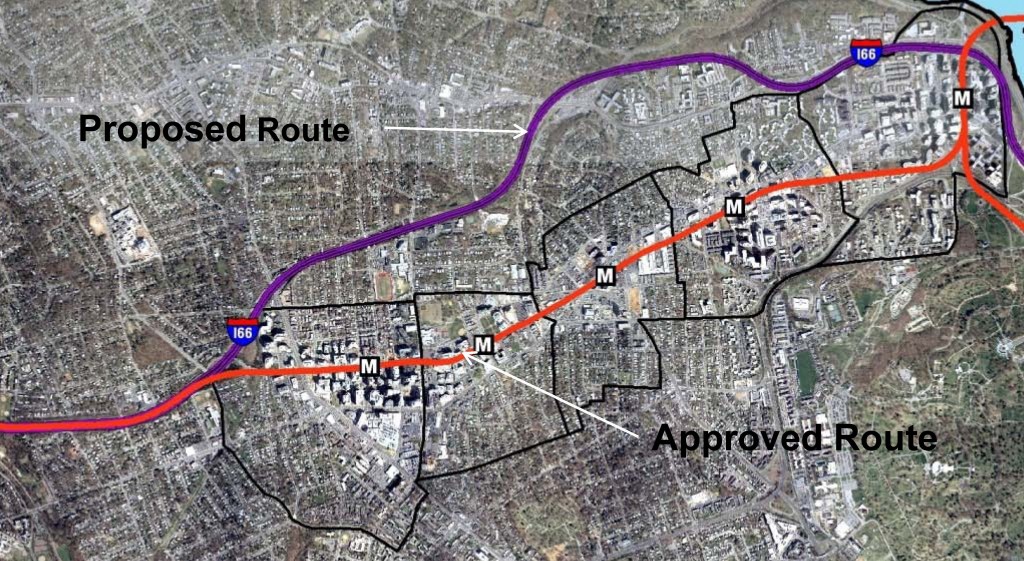
- The Silver Line extends Metrorail by over 20 miles, and will generate tens of thousands of new riders per day when Phase II opens – many of whom will travel into Metrorail’s already congested core.
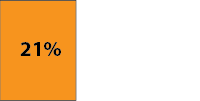
- The Columbia Pike Streetcar will transfer 32,000 riders per day to and from Metrorail at Pentagon City – at a point in the system that is already maxxed out.
- Two other planned busways (Crystal City/Potomac Yard, and Van Dorn/Beauregard) also connect with Metrorail stations.
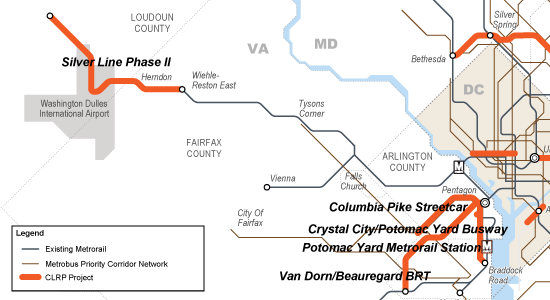
All major transit projects funded in the CLRP in Northern Virginia depend on the “backbone” of Metrorail and Metrobus.
By ensuring that Metro services can keep pace with congestion and demand, Metro 2025 is critical to making Virginia’s transit projects a success, and critical to helping the region and the state reach its transportation goals. Read more…





Recent Comments