Four reasons why we need to begin the Metro 2025 investments now.
1. Because Metro 2025 is critical for growth. For the last three decades, the Washington region has grown in lockstep with an expanding transit system. Since Metrorail opened in the late 1970s, the system has grown steadily, and in 2014 Metro provides two to three times more service (rail and bus vehicle-miles) than it once did.

For decades, this region has grown in lockstep with Metro.
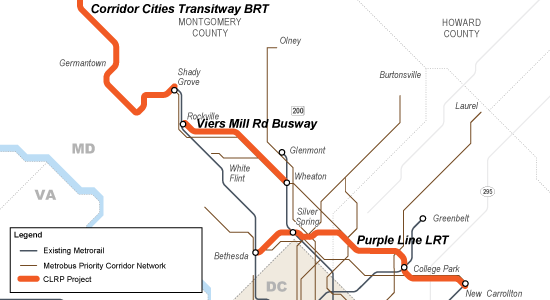
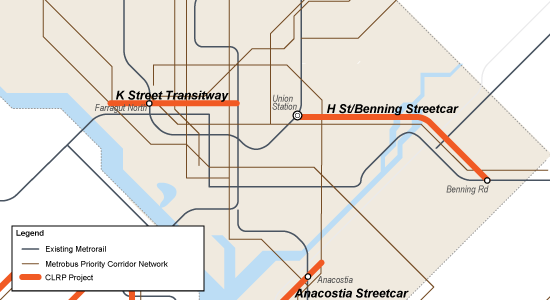
Today, no significant new Metro service is planned beyond the Silver Line, yet MWCOG estimates that the region will continue to grow at a steady clip for years to come. The only transit expansion projects that are planned complement and depend on connections to Metro, such as the Corridor Cities Transitway or Columbia Pike Streetcar, and may even increase the strain on Metrorail’s core.
2. Because we could lose jobs. Without investment in the region’s transit backbone, economic growth and prosperity is threatened. In fact, studies have shown a clear link between growing congestion and declines in job growth. Without Metro 2025, this region could stand to lose nearly 133,000 jobs by 2040.
3. Because Metrorail is crowded, and it will get worse without Metro 2025. Today, Metrorail is reaching its capacity in many places. On the Blue and Orange lines for instance, Metro is running trains every 2.5 minutes, which is the most the infrastructure can handle, but even so, many trains are too full to board, or experience uncomfortable levels of crowding. Lines form at many stations to get through escalators, elevators, and fare gates.
Without eight-car trains and fixing station bottlenecks, crowding and congestion on Metrorail will continue. The map below shows our projections of crowding (passengers per car) into the future, if we don’t undertake Metro 2025:

Crowding on Metrorail will worsen without the investments in Metro 2025. (Animated.)
4. Because Metrobus is stuck in traffic and needs relief. Metro’s buses are frequently caught in street traffic, which increases travel times, degrades reliability, and increases Metro’s operating costs just to maintain frequencies.
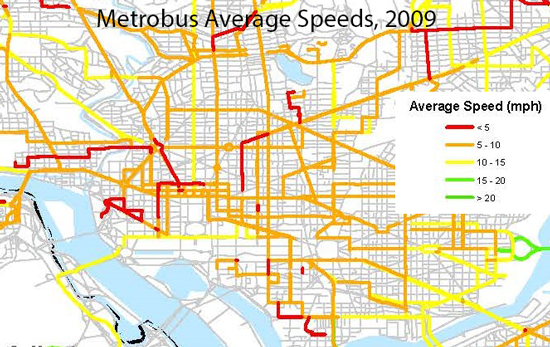
Illustration of Metrobus speeds from 2009. The red is 5 MPH or less. Click for full version.
In fact, numerous Metrobus corridors operate at speeds of less than 10 MPH, and several showed speeds of under 5 MPH. On many corridors, buses operate at a brisk walking pace even though they are carrying many more passengers than the traffic around them. On H and I Streets NW, buses carry 40% of the passengers but are only 2% of the vehicles. On 16th Street NW, buses carry 50% of the passengers, despite using just 3% of the vehicles.
To increase bus service, speeds, and reliability, we need to invest in bus-only lanes, bus priority at traffic signals, and additional buses.








Recent Comments