Funding Metro 2025 – Beyond Buzzwords
Fancy financing and accounting gymnastics won’t ride to the rescue for Metro 2025.
Public Private Partnerships. Tax Increment Financing. Infrastructure Banks.
These are among the many ideas discussed today as panaceas for public infrastructure funding, including major transit investment projects in the region and the nation. Certainly they can be helpful tools, especially in an era of declining federal funds and a renewed emphasis on local fiscal austerity. But can these tools be useful in funding or financing Metro 2025?

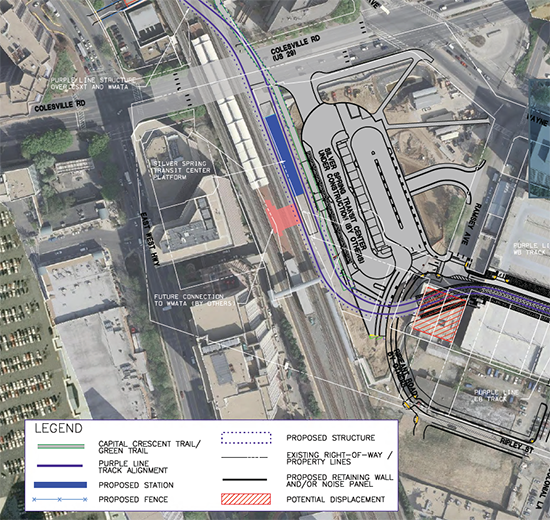
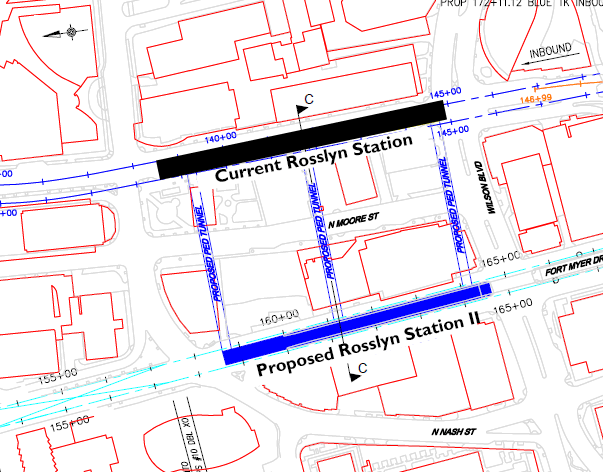
Spring Hill Silver Line Metrorail station. The Silver Line was financed in part by special tax districts.
Metro leadership wanted to find out, so between November 2013 and January 2014, Metro gathered leading experts in real estate, transportation and municipal financing from academe, management consulting, policy advocacy and government to solicit the best ideas for innovative ways of addressing Metro’s challenge. We learned that each of these financing techniques has differing strengths, weaknesses, and potential applications to capital projects. We also learned that none of the techniques actually provides new funding. Which is, ultimately, what is necessary to make Metro 2025 a reality.
The distinction between financing and funding cannot be overstated, and is a key concept that often confuses the dialogue surrounding how to execute major capital projects such as transit investments. Techniques such as Public-Private Partnerships, Infrastructure Banks, and Value Capture rely on existing sources of funding to channel and make more available monies to public entities to pay for varieties of projects. These existing sources of funding are often taxes – either on households, businesses, or property owners – and backstopped by jurisdictional guarantees to tap into general funds or issue general obligation bonds should the stream of cashflows become unstable. These financing techniques do not generate new monies nor eliminate the ultimate obligations of the public sector to provide the monies to contribute to the cashflows, either upfront or over time.
You can read more in the attached report, and know that Metro’s leadership is committed to evaluating any and all options to fund Metro 2025. Leaving no stone unturned, we conclude that as of this moment in time, regional leaders must step up to the plate and commit resources to Metro in order to make much-needed projects like eight-car trains, core station improvements, and the Metrobus Priority Corridor Network, leap off of the page and become part of the region’s transit network.
Download: Metro – Creative Financing (PDF, 1MB)



Recent Comments